NEW
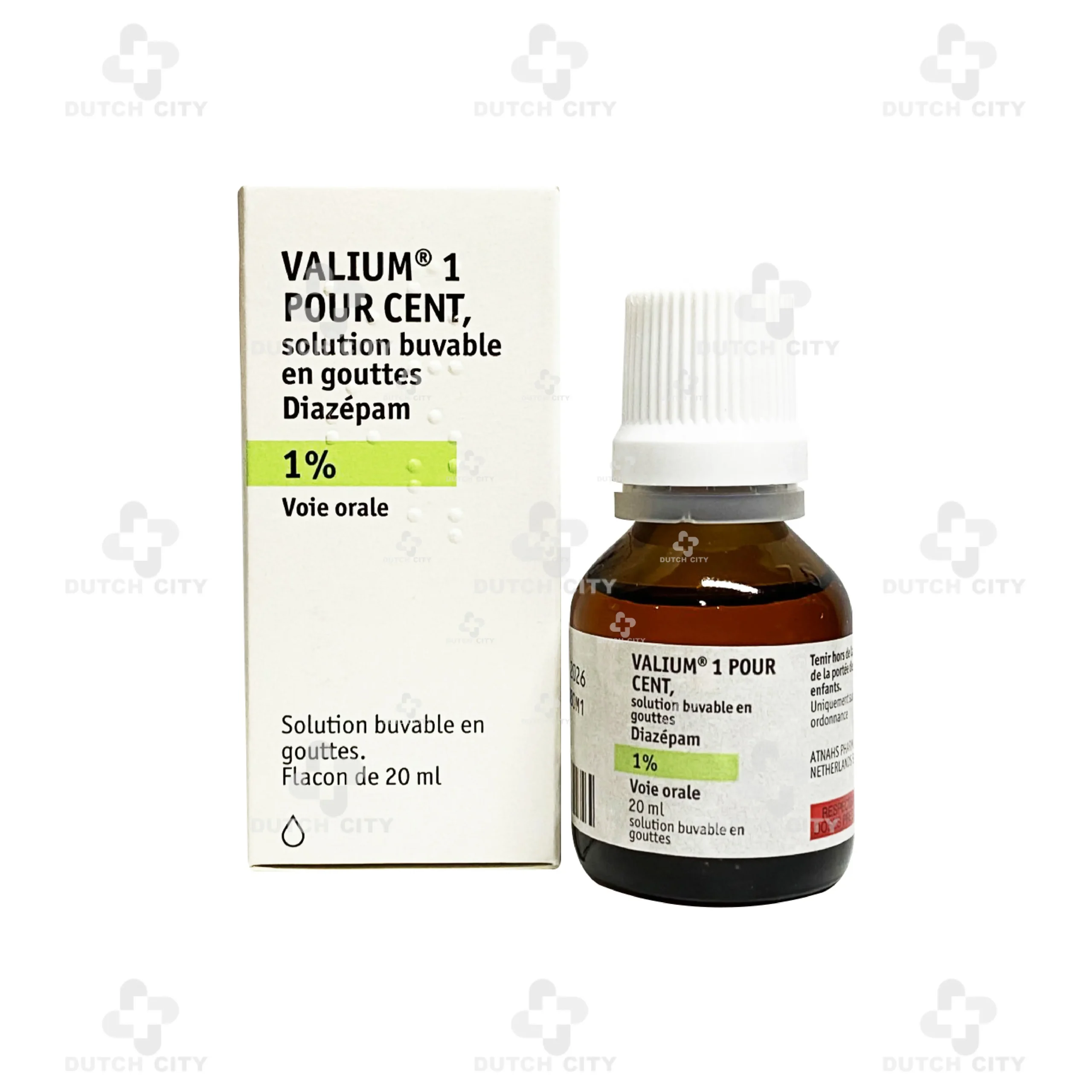
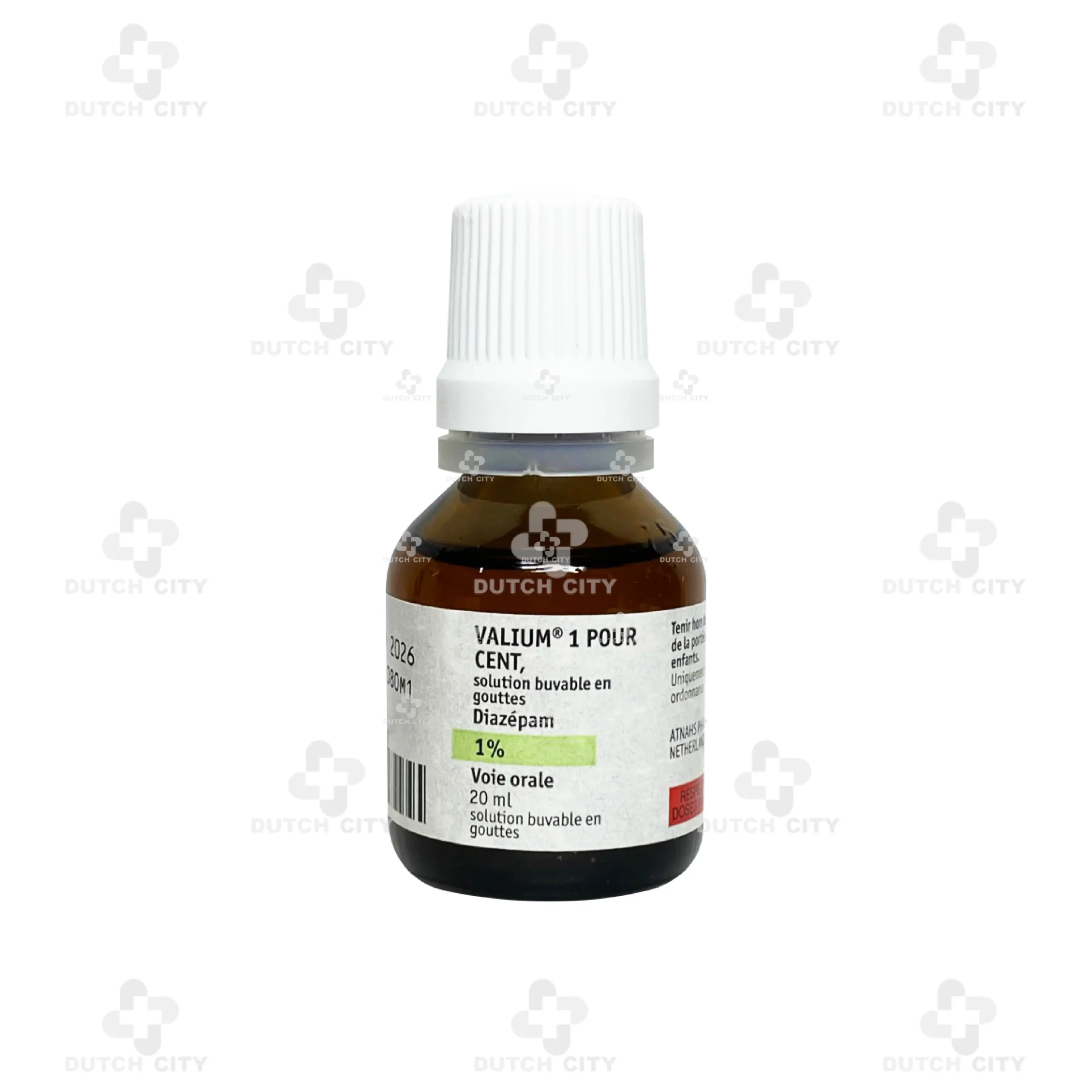
Valium® 1% 20ml 🇫🇷
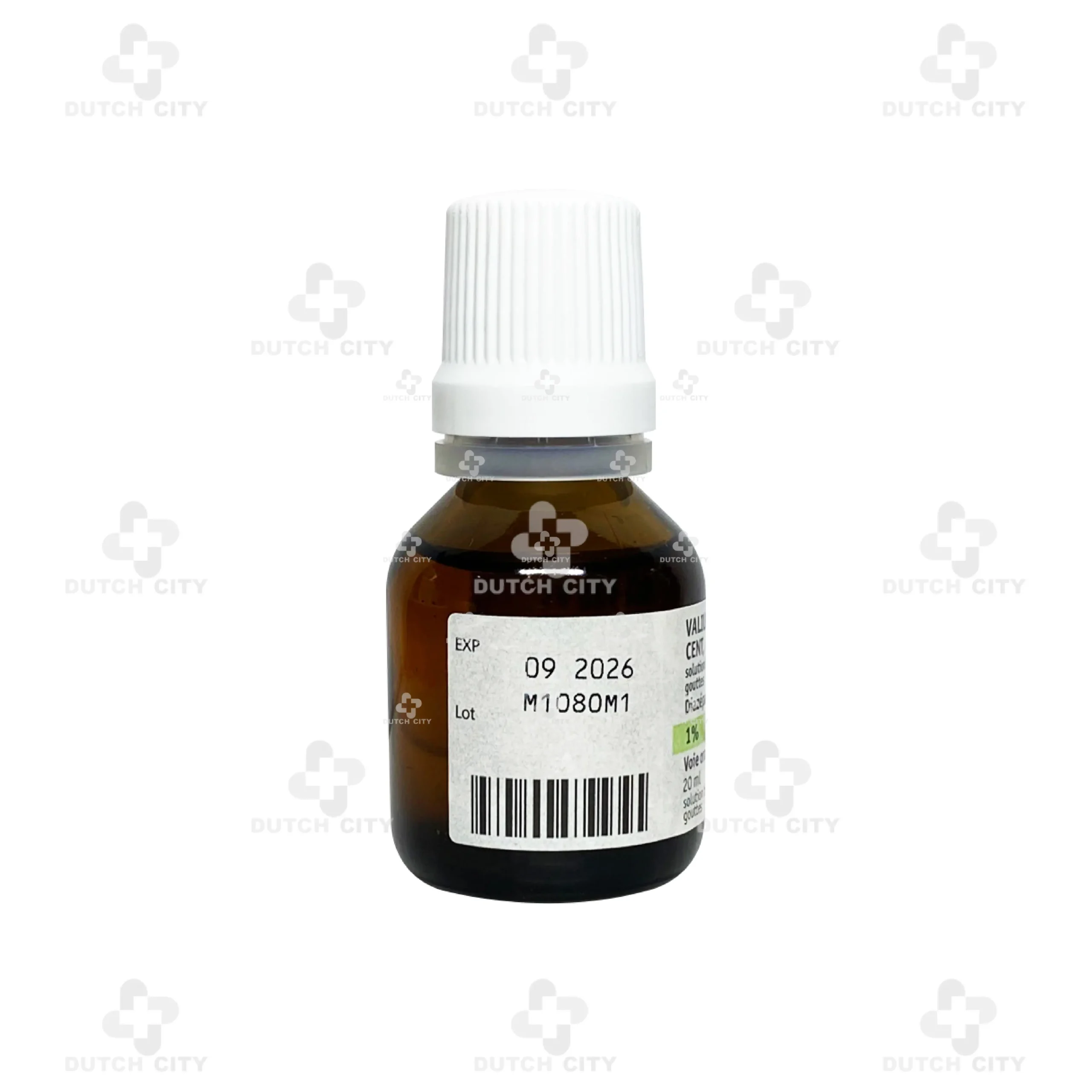
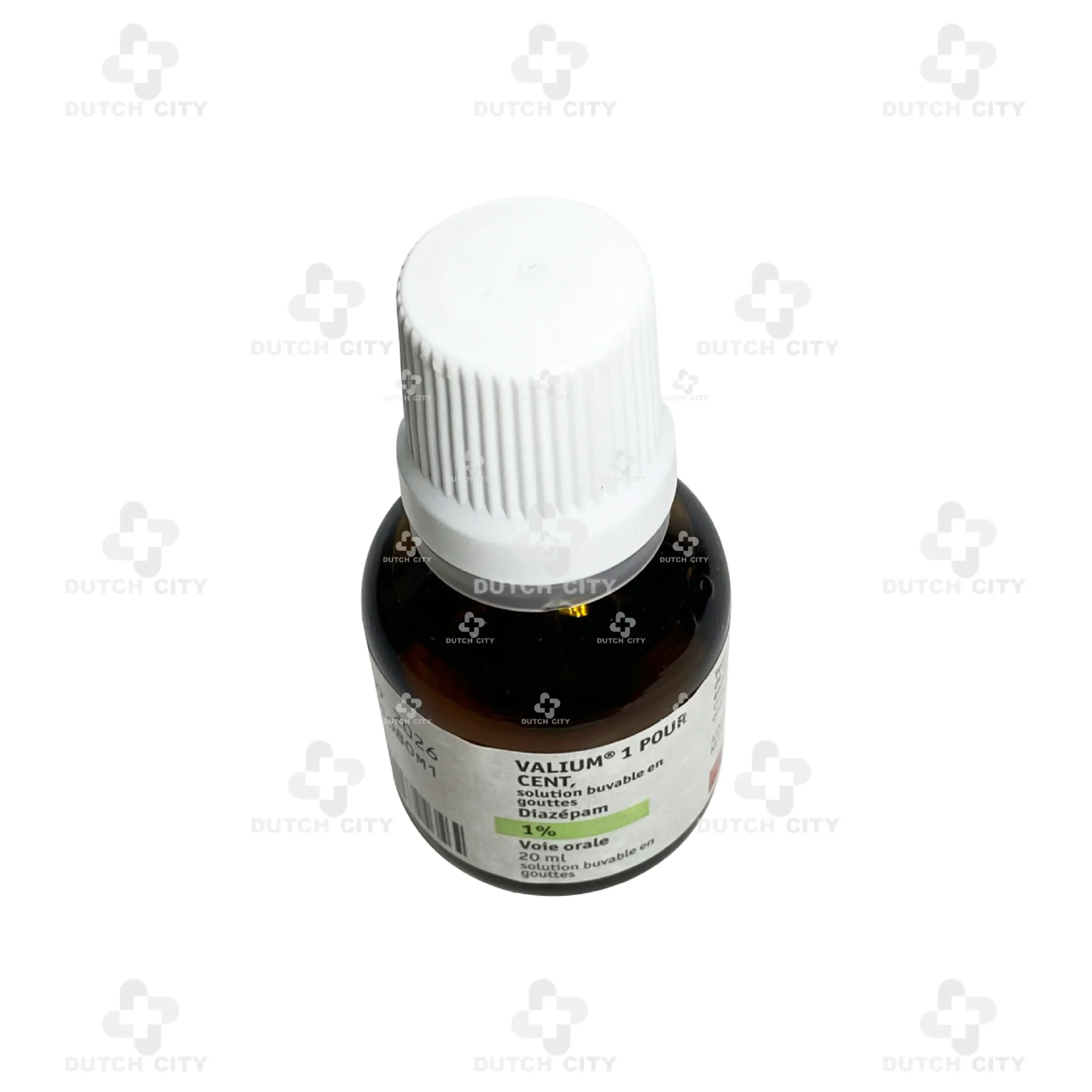
Valium® 1% Oral Solution (Drop form)
Active Ingredient
Diazepam – 1,000 mg per 100 ml (equivalent to 10 mg per 1 ml, ~30 drops)
Other Ingredients (Notable Excipients)
**Ethanol
**Sunset Yellow FCF (E110)
**Propylene Glycol
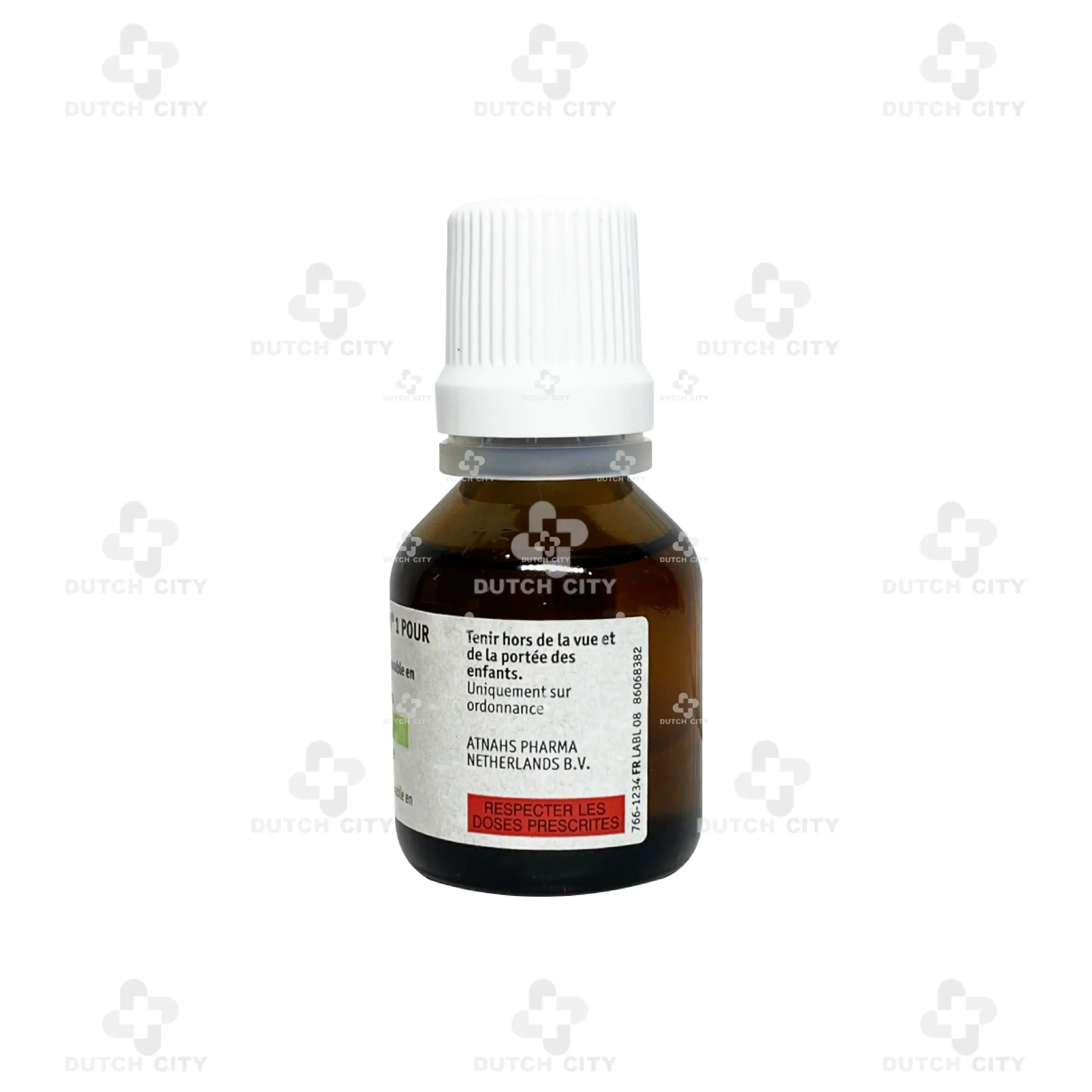
Manufacturer Information
Marketing Authorization Holder:
ATNAHS PHARMA NETHERLANDS B.V.
Copenhagen Towers, Ørestads Boulevard 108, 5.TV,
DK-2300 Copenhagen S, Denmark
Manufacturer:
Centre Spécialités Pharmaceutiques
76/78 Avenue du Midi, 63800 Cournon d’Auvergne, France
Pack Size: 20 mL
#Benzodiazepines , #Benzodiazepine, #benzo , #benzos , #Benzo , #Benzos , #BENZO, #BENZOS





























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.