NEW
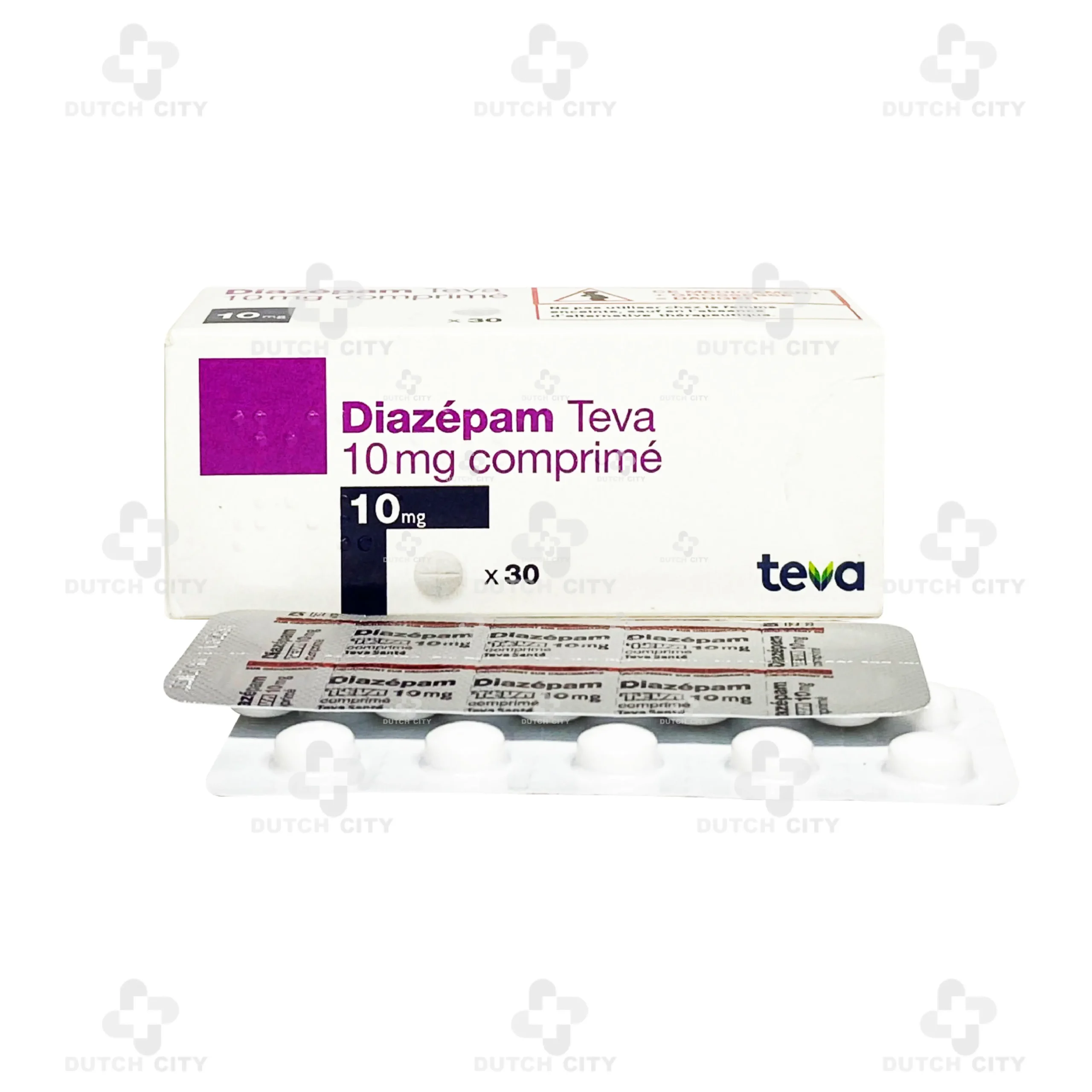
Diazepam TEVA 10mg 🇫🇷
Diazepam TEVA 10mg 🇫🇷
Product Name and Active Ingredient
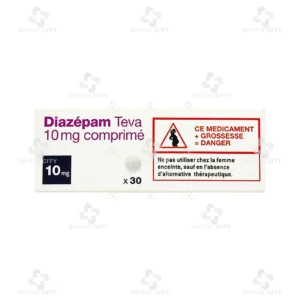
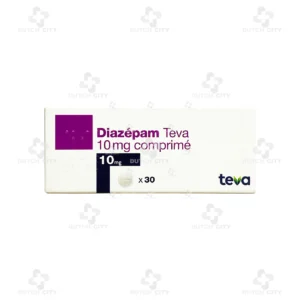
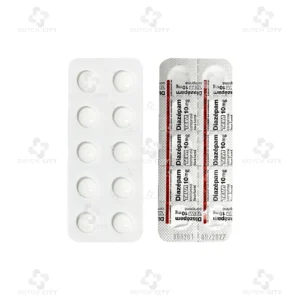
Brand Name: Diazepam TEVA 10mg
Active Ingredient: Diazepam
Pharmacological Class: benzodiazepine
Composition
Active Ingredient: Diazepam 10 mg per tablet
Manufacturer and Country of Origin
Manufacturer: Teva Czech Industries, s.r.o. – Opava‑Komarov, Czech Republic
Country of Origin: France
(1 box – 3 strips or 30 tablets)
#Benzodiazepines , #Benzodiazepine, #benzo , #benzos , #Benzo , #Benzos , #BENZO, #BENZOS,























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.